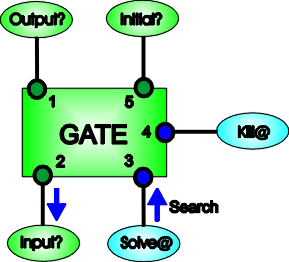

The format of the GATE External function is:
GATE( Input?, Solve@, Kill@, Initial?)
The function provides a way of storing and remembering information from one cycle to
the next, and normally obtains its timing information from a looping function like WHILE.
In normal programming terms, the operation of a loop may be visualised as follows (the
example is a WHILE loop, a FOR loop would be similar):
a := initial_value WHILE a < 9 DO a := a + 3
In a knowledge network, a := a + 3 is not a valid statement as the variable
"a" can have only one value at a time, and in changing its value, the old value
is lost.
The GATE Function is provided to handle the storing of a value under control of timing
signals. The function is usually used in conjunction with a loop function such as FOR or
WHILE, which provides the necessary phasing of the Solve@ and Kill@ signals.
The parameters of the GATE Function are:
In operation, searching comes in on link 3 (Solve@), linked to the Test@ pin of a WHILE
function.
What happens next is:
Copying of the Input? value involves creating constants to represent the Input information in a similar way to the EVAL function, but these constants are not destroyed when the input list is destroyed.
GATE is not suitable for moving values through an undo, as with GENERATE - all its
stored values will be undone.
Related Functions
| LATCH |